The Big Picture
Singapore's real GDP per person has grown incredibly since independence in 1965, helping the country make the leap from third world to first world in less than half a century.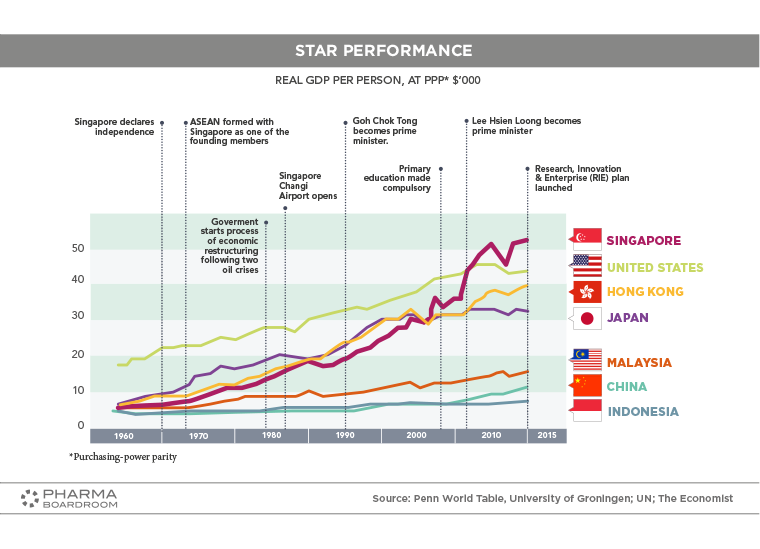
Switzerland is the world's leading nation for investor friendliness in terms of ease of doing business, labour force, and innovation input.
Singapore is home to over 40 percent of global MNCs' regional headquarters.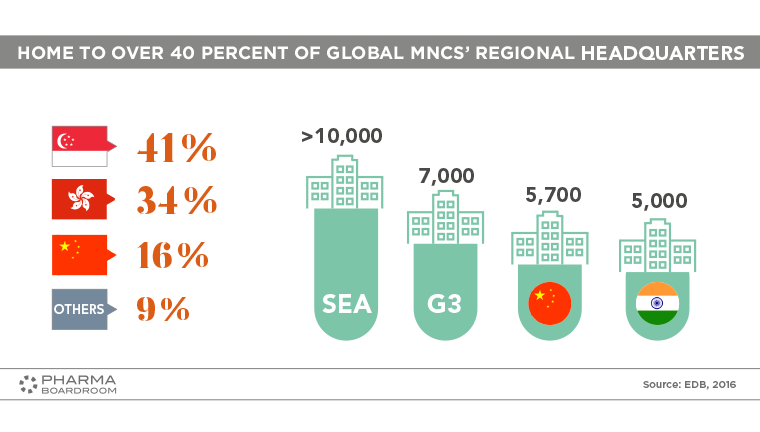
Health Profile The healthcare landscape in Singapore is rapidly changing, with an aging population necessitating a dramatic increase in demand for healthcare workers.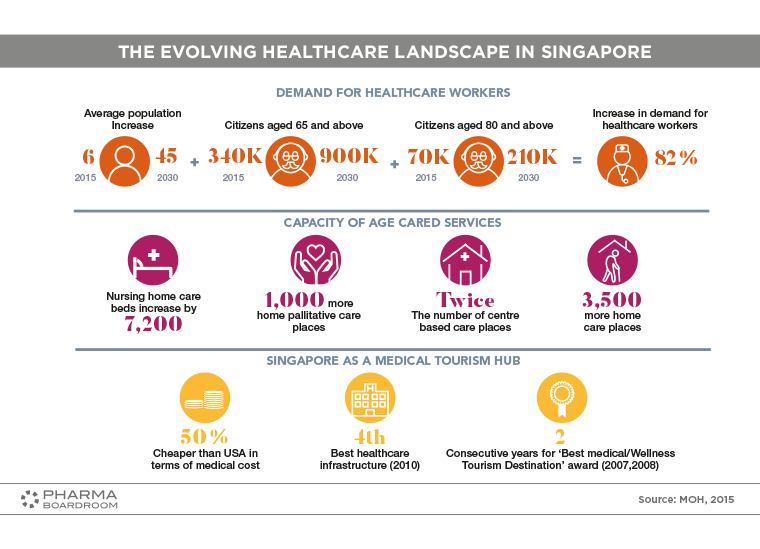
Asia is aging rapidly. This demographic shift will have profound consequences on healthcare dynamics throughout the region.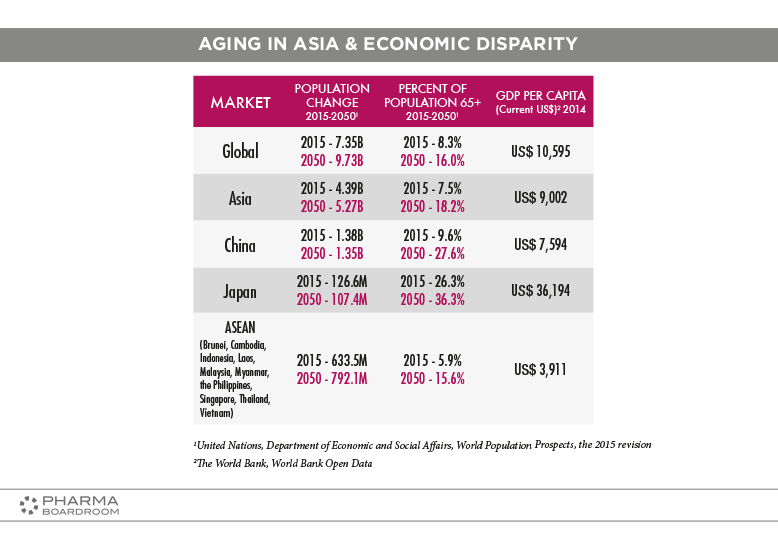
The Top 10 causes of death per year in Singapore: coronary heart disease and influenza and pneumonia are the most prevalent.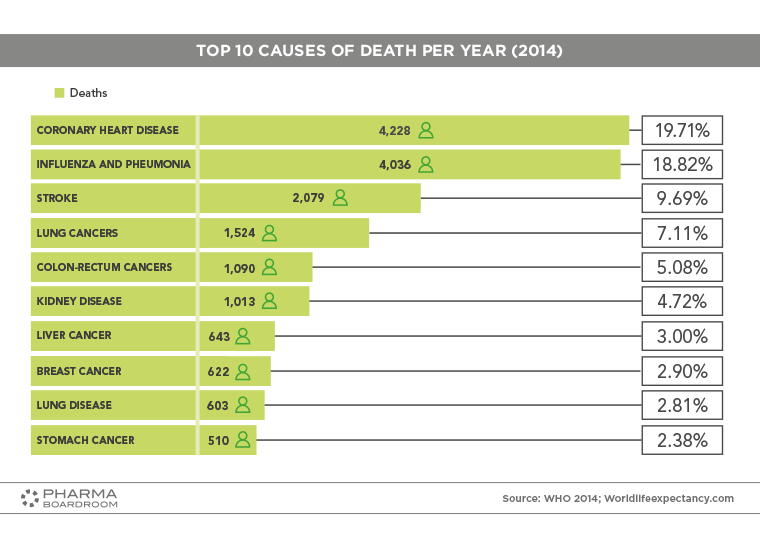
Singapore is by far the most developed and efficient healthcare provider in ASEAN and annually spends the most per capita on health.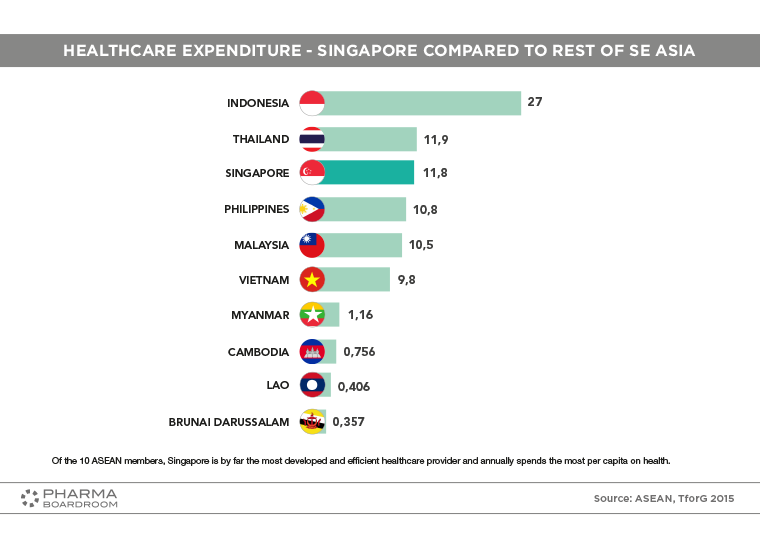
Health risk factors in Singapore: smoking, alcohol consumption, and obesity.
Pharmaceutical Industry Manufacturing as a percentage of GDP remains high in Singapore, especially compared to fellow Asian Tiger Hong Kong which has divested most of its manufacturing capabilities.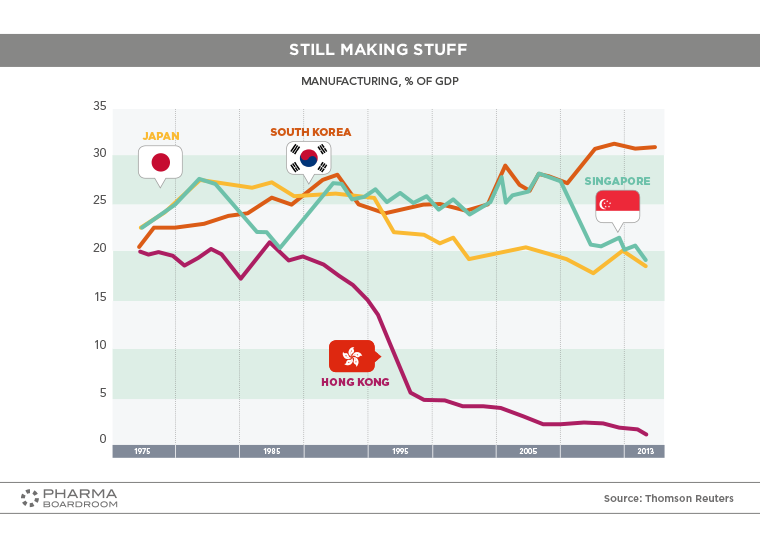
Biomedicals and chemicals make up a significant section of Singapore's manufacturing output.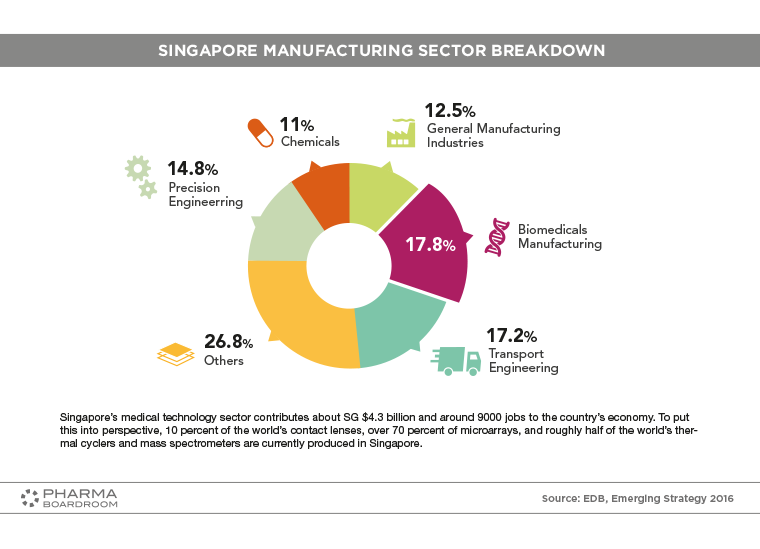
Generics penetration in Singapore is low compared to its regional neighbours.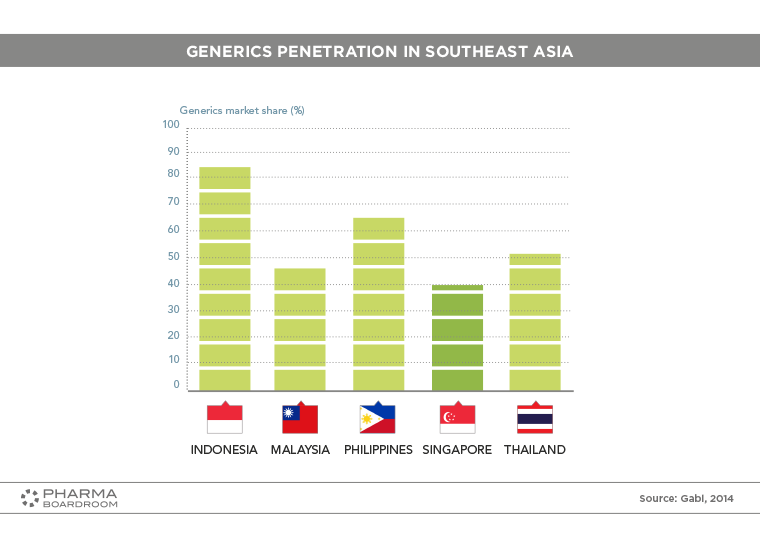
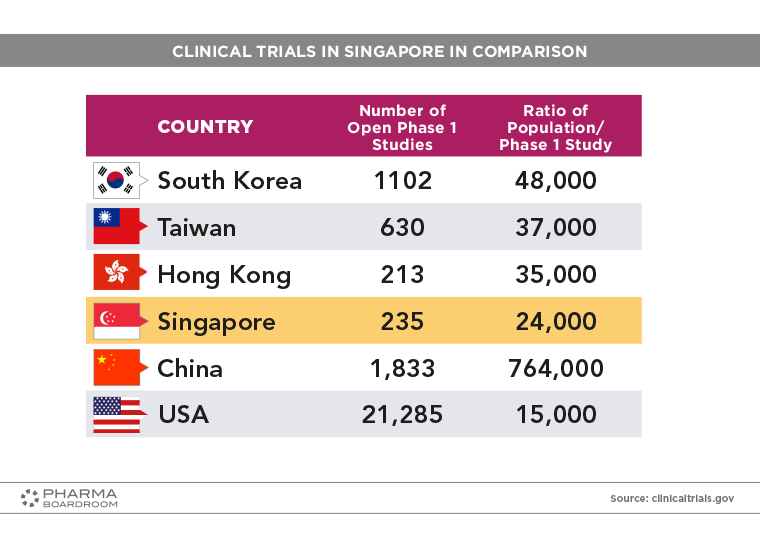
Singapore's export sector has gradually reduced in volume since the turn of the millennium, but pharmaceuticals could represent an opportunity to help revive it.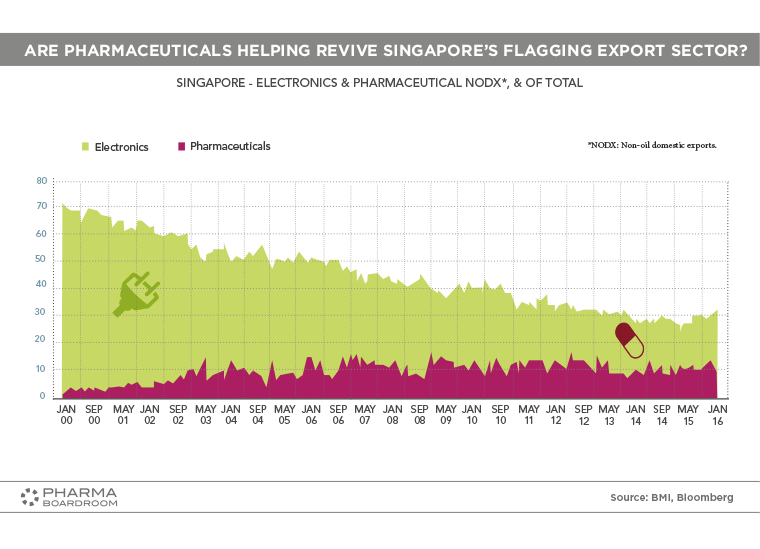 Clinical trials in Singapore in international comparison.
Clinical trials in Singapore in international comparison.
BioSciences Singapore's biomedical sciences industry spreads across the island, with a number of key hubs clustering together many of the APAC headquarters for major pharma and biotech MNCs.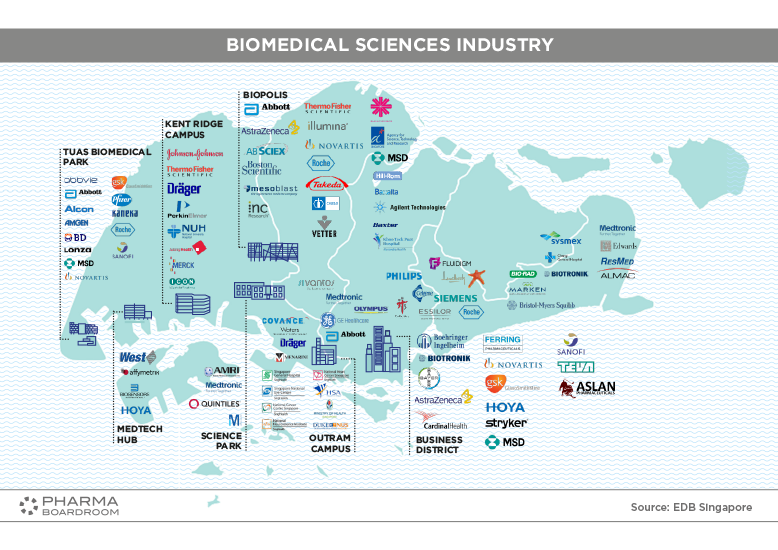
Singapore has surged to fifth position in Scientific American's global biotech rankings and also fares well in terms of R&D intensity, number of researchers per million people, and bioscience patent applications.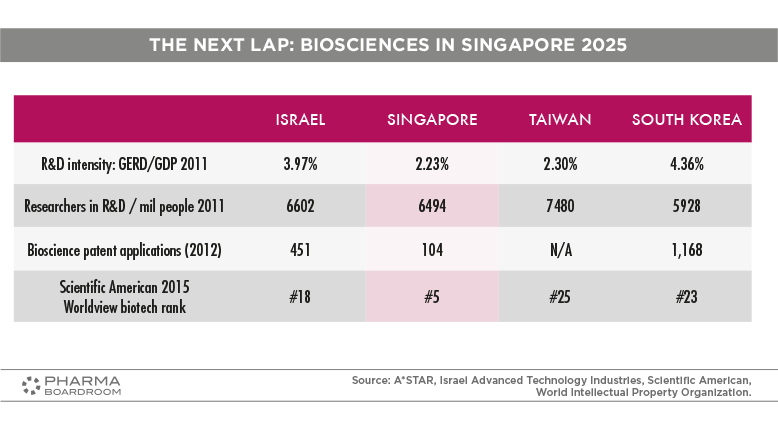

Singapore's real GDP per person has grown incredibly since independence in 1965, helping the country make the leap from third world to first world in less than half a century.

Switzerland is the world's leading nation for investor friendliness in terms of ease of doing business, labour force, and innovation input.

Singapore is home to over 40 percent of global MNCs' regional headquarters.

Health Profile The healthcare landscape in Singapore is rapidly changing, with an aging population necessitating a dramatic increase in demand for healthcare workers.

Asia is aging rapidly. This demographic shift will have profound consequences on healthcare dynamics throughout the region.

The Top 10 causes of death per year in Singapore: coronary heart disease and influenza and pneumonia are the most prevalent.

Singapore is by far the most developed and efficient healthcare provider in ASEAN and annually spends the most per capita on health.

Health risk factors in Singapore: smoking, alcohol consumption, and obesity.

Pharmaceutical Industry Manufacturing as a percentage of GDP remains high in Singapore, especially compared to fellow Asian Tiger Hong Kong which has divested most of its manufacturing capabilities.

Biomedicals and chemicals make up a significant section of Singapore's manufacturing output.

Generics penetration in Singapore is low compared to its regional neighbours.

Singapore's export sector has gradually reduced in volume since the turn of the millennium, but pharmaceuticals could represent an opportunity to help revive it.
 Clinical trials in Singapore in international comparison.
Clinical trials in Singapore in international comparison.

BioSciences Singapore's biomedical sciences industry spreads across the island, with a number of key hubs clustering together many of the APAC headquarters for major pharma and biotech MNCs.

Singapore has surged to fifth position in Scientific American's global biotech rankings and also fares well in terms of R&D intensity, number of researchers per million people, and bioscience patent applications.